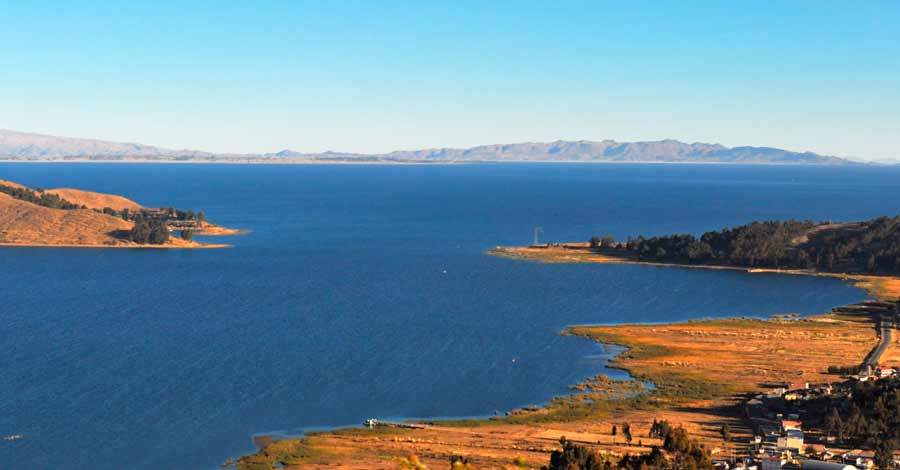
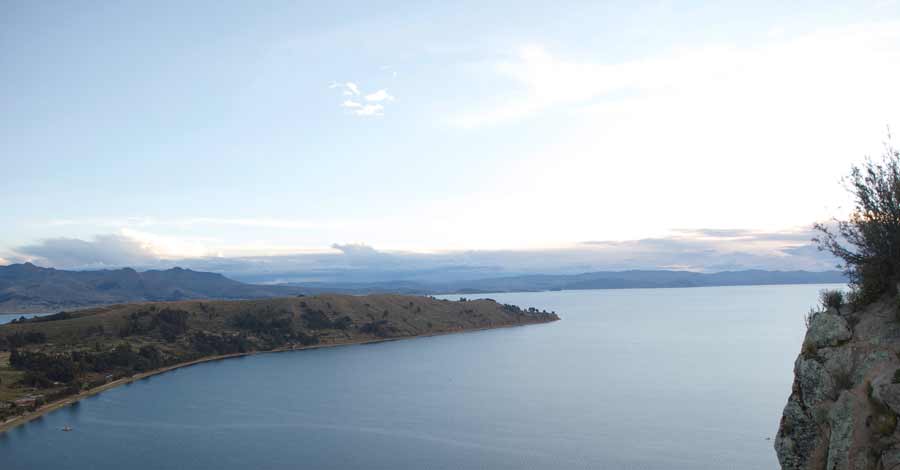
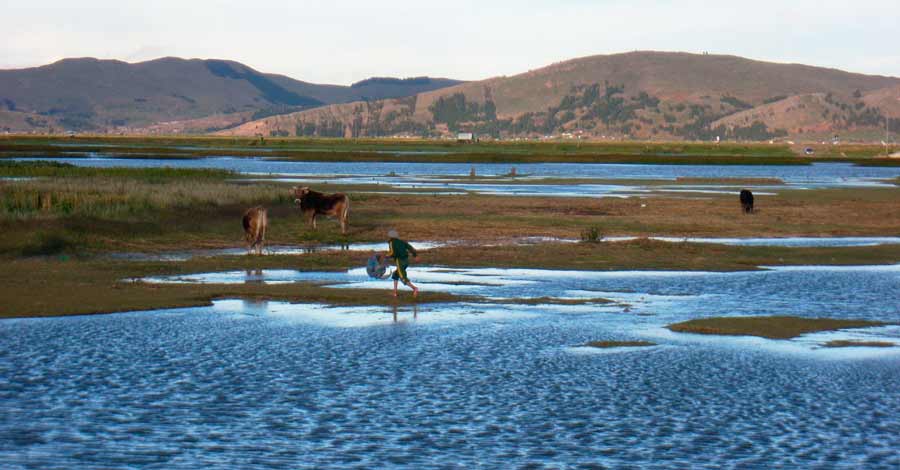
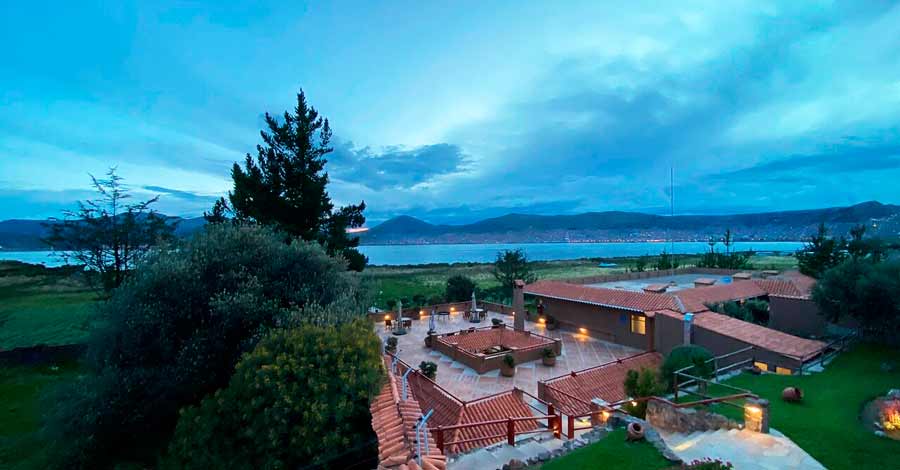
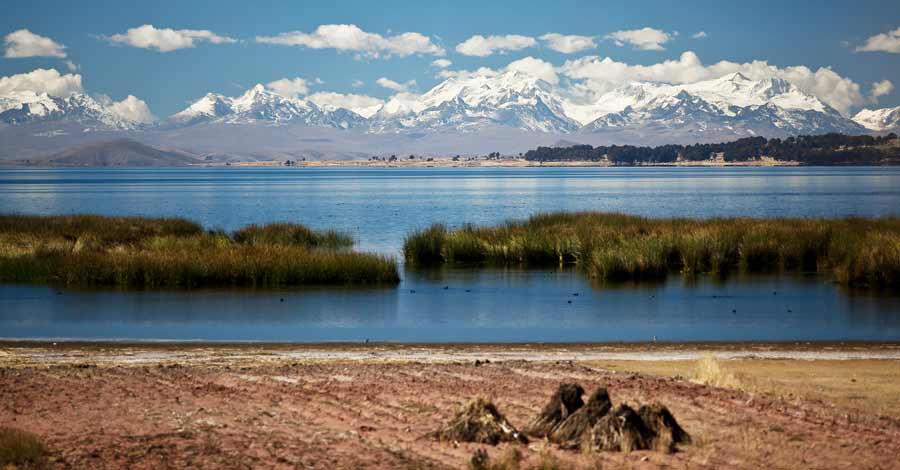
Considered the highest navigable lake in the world, Lake Titicaca is a spectacle wherever you look at it, it preserves the identity and history of two countries in its cold waters of green, blue, turquoise, and gray tones in the middle of imposing Andean snow-capped mountains. Discover with Auri Peru some of the most striking and little-known aspects of the great Lake Titicaca, the cradle of the Andean civilization.
What is lake Titicaca?
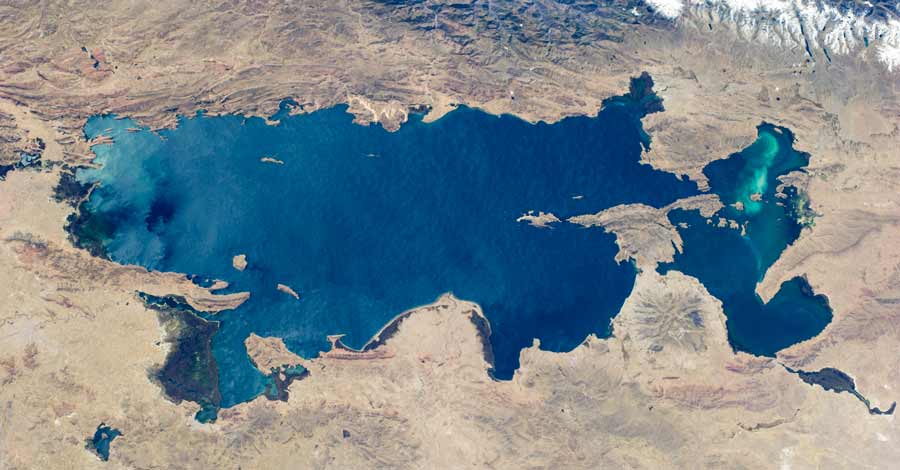
Lake Titicaca, known in Spanish as “Lago Titicaca”, is the highest navigable lake in the world. Its waters are crossed by launches, boats, small cruisers and above all handcrafted and traditional boats made of totora reeds. It is home to a number of myths and legends as well as numerous mysteries. Titicaca is the second largest lake in South America after Maracaibo, the sweetest lake in South America and it is the 19th largest lake in the world in terms of extension.
Lake Titicaca is the ancestral land of the Quechua, Aymara, Uros, Pacajes and Puquinas ethnic groups. Lake Titicaca was the cradle of the most influential pre-Hispanic cultures of the entire Andean region. The entire lake is a protected reserve and is home to numerous migratory and aquatic birds.
Where is lake Titicaca?
This natural wonder, declared Natural Heritage of Peru, is located in the Collao plateau. Lake Titicaca is located in southeastern Peru, near the border with Bolivia in South America. Lake Titicaca is located in a high plateau of the Andes mountain range at latitude 14º south. In this area, the Andes chain separates into two mountain ranges that delimit between them a high plateau of approximately 200,000 km2 located between 3,600 and 4,500 meters. Lake Titicaca occupies the northern part of this gigantic plateau called Andean Altiplano.
Where is lake Titicaca located? Is lake Titicaca in Peru?
Lake Titicaca is located between the countries of Peru and Bolivia, in the region of Puno in Peru, which in turn is shared with the department of La Paz in Bolivia. Lake Titicaca has 56% of Peruvian nationality and 44% of Bolivian nationality, is a binational lake.
How high is lake Titicaca above sea level?
Lake Titicaca is 3812 meters above sea level or its equivalent of 12507 feet of altitude. According to Peruvian geographer Javier Pulgar Vidal, eight natural regions can be identified in Peru according to their altitudinal floors, to which correspond certain climatic conditions, relief, flora, fauna and resources. Lake Titicaca corresponds to the altitudinal level of the Suni region.
How large is lake Titicaca? How large is lake Titicaca in km?
Lake Titicaca has an area of 8 562 km² and its dimensions cover 204 kilometers / 127 miles from side to side with an extension of 1125 kilometers of shoreline bordering its entire surface. The total volume of water in Lake Titicaca is 903 cubic kilometers. Lake Titicaca, it is divided into two lake basins:
- The “Minor Lake” or Huiñaimarca.
- The ” Major Lake” or Chucuito.
These two parts are joined by the Tiquina Strait, which is 800 meters wide and has a minimum depth of 21 meters.
How deep is lake Titicaca?
We can divide the depth of Lake Titicaca according to its two lake basins. The maximum depth of Major Lake is 281 meters and that of Minor Lake is only 40 meters. More than two-thirds of the Major Lake is deeper than 150 meters while the Minor Lake is only 5 to 10 meters deep in most of its extension. Therefore, the maximum depth of Lake Titicaca is 281 meters.
Weather at lake Titicaca
The climate of Lake Titicaca is temperate during the day and cold at night due to the altitude. Because of its altitude, it is influenced by conditions characteristic of mountain climates (high light intensity, low temperatures, low humidity). During the day it reaches 24°C on average and the nights are cold, the winds over the lake give an average surface temperature of 9°C or less. Temperatures varies dramatically between day and night. It has been determined that the average annual temperature of the lake is 13 °C.
How old is lake Titicaca?
Regarding the origin of Lake Titicaca, we must necessarily refer to the appearance of the Andes mountain range thanks to the movement of plate tectonics, those mechanical forces originated by the geothermal force of the earth’s magma.
Before the formation of Lake Titicaca, this territory was located under the sea, on the seabed. During the uplift of the Andes Mountains, the Collao plateau was formed, which trapped a portion of the sea. This type of flat and level relief, which after the uplift rose to an altitude of more than 3000 meters, kept the waters frozen in its interior during the ice age. This allowed it to maintain its shape and depth, so that when the interglacial period occurred, these ice masses thawed and became what was probably an inland sea.
The Titicaca we see today is the remainder of that gigantic lake or older sea, which receded to its current extent. This process took thousands of years, the age of the current Lake Titicaca is estimated at 3 million years.
Etymology of Titicaca, which means the name of the Titicaca lake?
In relation to the name of the lake, Titi, which means cat or puma, and kaka, stone. This would mean “the lake of the stone pumas” or “stone puma”. A popular myth tells that the pumas were sent by the deities of the mountains, the Apus, to devour human beings after they made an offering by climbing to the top of the mountains, which was forbidden. After these events, the sun god Inti cried for 40 days and 40 nights forming Lake Titicaca. After this, the pumas were turned into stone.
Other legends about the origin of the name of Lake Titicaca
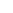
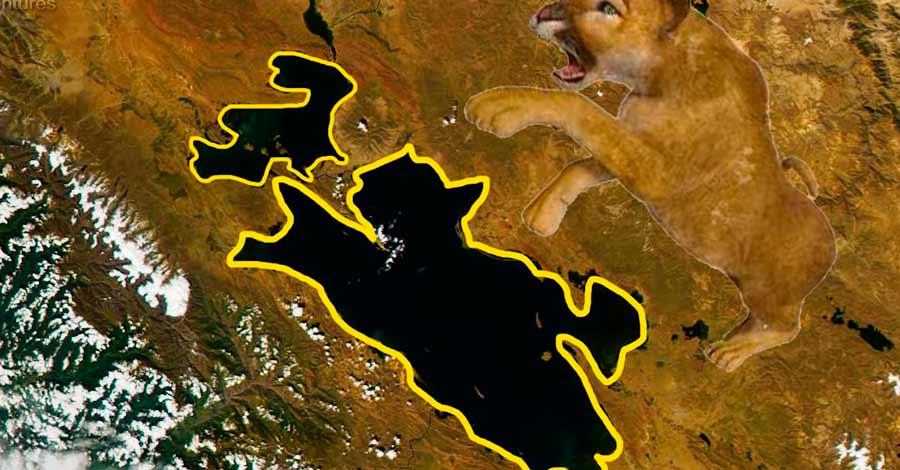
There is a very curious fact about Lake Titicaca. In 1973, the artificial satellite Gemini took the first photograph of Lake Titicaca from space, and it was discovered that the lake has the shape of a puma at the moment of catching its prey, a vizcacha.
Others point the origin of its name to the name of the island Intikjarka, which is derived from the Aymara and Quechua languages and means Inti (sun) and Kjarka (rock), even refers to the ancient name of Titikaka was formerly the name of the island of the Sun, which also took the name of the lake later. Curiously, there is a sacred rock on the Island of the Sun from where, according to Quechua and Aymara legends, the sun, the moon and the stars emerged. This rock is also mentioned as the “paqarina” or place of origin of the Inca ethnic group.
There are some other legends that say that the waters of Lake Titicaca hide cities with abundant gold and silver, or that in its waters live mermaids that attract death with their singing. These and many other stories are the perfect accompaniment to visit and navigate these waters full of mythology and Andean tradition.
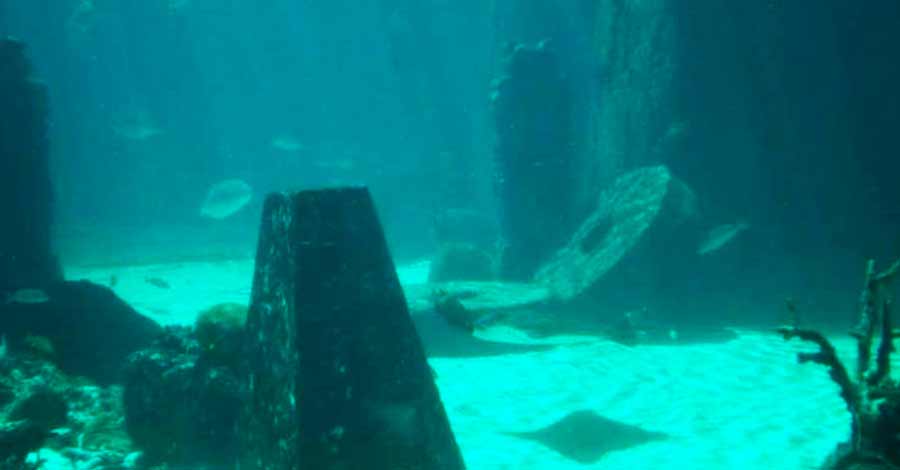
A sunken city in Lake Titikaka?
Some legends about the origin of the name of Lake Titicaca are very old and probably related to a feline idol that represented the sun in a city that was sunken in the lake. An interesting fact is that during an expedition made up of Peruvian navy divers and oceanography experts during the month of October 2002, remains of what could be a lost and submerged city were found in the waters of Titicaca. A city probably built by a predecessor of the Inca society under the waters of Lake Titicaca.
What is special about lake Titicaca?
Lake Titicaca is the highest navigable lake in the world. Lake Titicaca contains a great natural and cultural wealth, in its waters we find a great variety of flora and fauna endemic to the region. One of the most widespread things about this lake is that it is a binational lake, home of many myths and legends about the origin of Andean man and cradle, according to Garcilazo, of the most prolific civilization that inhabited South America, the Incas. Titicaca also hides great secrets about the history of many societies that inhabited its surroundings.
How many rivers empty into lake Titicaca?
The highest navigable lake in the world is a spectacle wherever you look at it. It has about 25 tributary rivers adding Peruvian and Bolivian territory. The main tributary rivers of Lake Titicaca are the Ramis, Ilave, Coata, Catari, Huancané and Suchez. The length of these main rivers is between 120 and 180 km, with the exception of the Ramis River, which is 283 km long. The secondary tributaries are the Ilipa, Yanarico, Zapatilla rivers (in Peru); Huayco, Putina, Keka, Khullu Cachi, Sehuenca and Tiahuanacu (in Bolivia).
The effluent is the Desaguadero River, which starts in the Bolivian part of Lake Titicaca and after a 398 km journey flows into Lake Poopó, with a height difference of 124 meters above the level of Lake Titicaca.
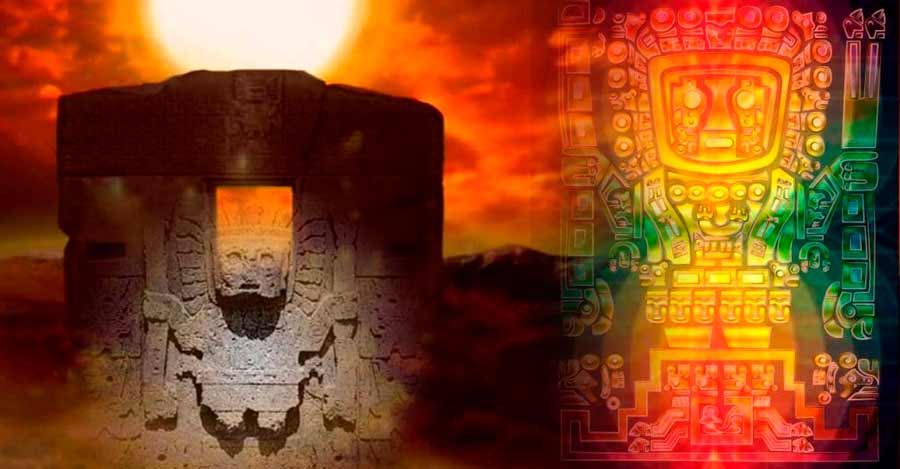
Wiracocha, the divinity that emerged from the lake Titicaca
The Incas were polytheists, they worshipped several deities of nature, among them the Inti or sun god. Another superior divinity that they integrated into their culture was the god Wiracocha, the creator of all things in the universe according to the legends. Wiracocha became a parallel god throughout the Peruvian-Bolivian highlands, even equal to the Christian God. The full name of Wiracocha is “Apu qon illa tiqsi wiraqucha pachayachachiq”.
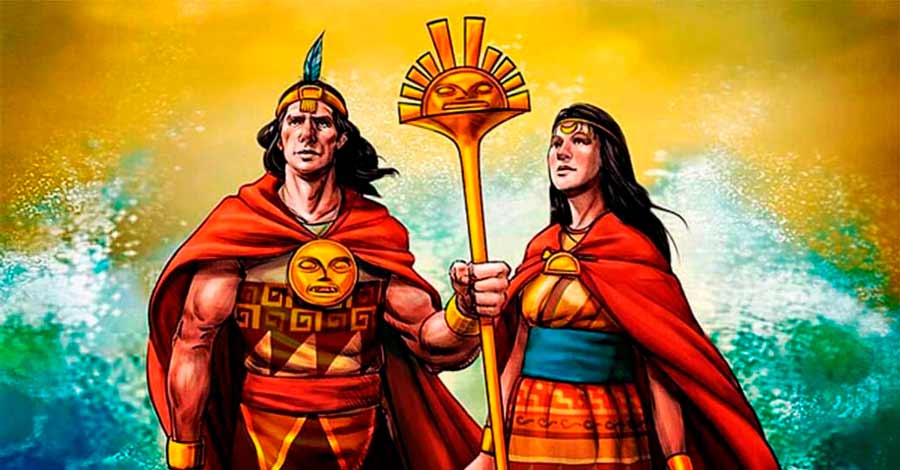
According to Andean tradition, Lake Titicaca was the place where the world was created, when the god Viracocha came out of the lake and created the sun, the stars and the first people. Wiracocha then traveled across the continent and disappeared in the waters of the ocean. Today, Lake Titicaca is still the cradle of Andean traditions and customs that can be discovered in a few days.
Brief history of lake Titicaca
The Titicaca altiplano began to be populated around 10,000 years before Christ, when small groups of people traveled the territory dedicated to hunting and gathering food. Regarding the groups that settled on the shores of Lake Titicaca, one of the most important cultures that settled on the shores of Lake Titicaca was the Chiripa culture, of which there are important archaeological remains in the southern part of the lake. Similarly, to the north of the lake, the Pucara culture developed with important similarities. It is believed that the domestication of some tubers and South American camelids (alpaca and llama) began around Lake Titicaca.
Around 45 A.D., the urban period of the Tiahuanacota culture dominated Lake Titicaca, building important ceremonial centers on the islands and around the lake. As already mentioned, some chroniclers describe the legendary origin of the Incas in Lake Titicaca, in the oral traditions of the area is still considered the island of the Sun as the place where the legendary Manco Capac and Mama Ocllo left to found the Tahuantinsuyo. The truth is that Lake Titicaca had great religious importance in Inca society. Pachacutec was the one who annexed Lake Titicaca and its surroundings to the Tahuantinsuyo.
According to Uros traditions, they fled from the Inca siege by taking refuge in the lake, for this purpose they built artificial islands in the lake using totora reeds as raw material. This is how the population of the floating islands of the Urus began in Peru. Since the creation of the viceroyalty of Peru in 1542, the lake was administered by Spain. With the independence of Peru and Bolivia, the division of Lake Titicaca became binational.
Flora and fauna of Lake Titicaca
According to the Titicaca National Reserve, there are 159 registered species of fauna, of which 15 are mammals, 105 are birds, 9 are amphibians, 4 are reptiles and more than 26 are fish. The endemic grebe or keñola, the choka, the tikicho and wild ducks stand out. You can also observe the maquerancho or yanavico, the parihuanas, the Totora Sietecolores and many others. A total of 171 plant species have been found in and around Titicaca. The most outstanding is undoubtedly the totora reed.
Among the native fish of Lake Titicaca are threatened species such as the boga, suche and mauri. The introduced species that are of great commercial value are the trout and the pejerrey, which in addition are the main causes of the decrease in the population of native species.
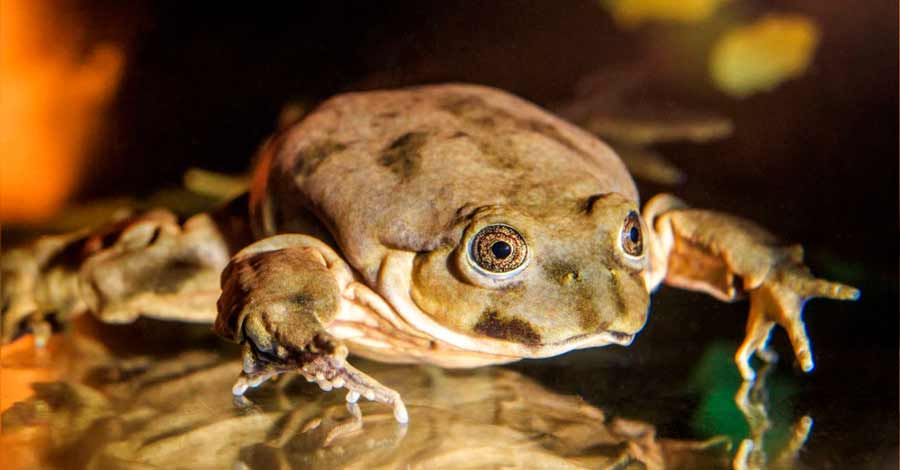
The lake Titicaca frog
The giant Titicaca frog is the largest exclusively aquatic amphibian on the planet. It inhabits Lake Titicaca and is, without a doubt, the most outstanding endemic species of the famous Lake Titicaca. An endemic frog whose habitat is mostly the depths of Lake Titicaca. This frog is critically endangered and is listed in the numismatic series of Endangered Wild Fauna of Peru.
In its adult stage, the Titicaca giant frog, whose Aymara name is Jamphatu Huankele, can reach more than 14 centimeters. Individuals of 30 to 50 centimeters have even been recorded. Their size varies depending on the area where they are found.
These frogs have a large body and a rounded, broad and flattened head. Like other species of the same genus, they “sing”. But what makes them different is that they are the only ones of their genus that have cannibalistic behaviors.
How to get to lake Titicaca from the Peruvian side?
Traveling to Lake Titicaca in Puno by Airplane
In case you want to get to Titicaca in the fastest and most convenient way, there is the method of air transportation through Puno which has an airport in the province of San Roman in the district of Juliaca.
The Puno airport receives planes from Lima, Arequipa and Cusco; all visitors looking for Lake Titicaca or visiting the city, pass through the Juliaca airport which is 1 hour from the city of Puno, i.e. Lake Titicaca. Flights from Arequipa or Cusco make a necessary stopover in the city of Lima. The duration of the trip from Lima to Puno is 1 hour and 30 minutes.
Traveling to Lake Titicaca in Puno by Bus
To get to Puno and visit the beautiful Titicaca by bus there are different routes, 4 in total.
One from Lima, one from Cusco and two from Arequipa. From Arequipa, one of these bus routes leaves from the town of Chivay (Colca Canyon).
From Lima to Puno by bus
In this case there are many companies that provide transportation service to Puno, two of the best known are Cruz del Sur and Civa. The trip from Arequipa is divided into two parts, from Lima to Arequipa is 16 hours and from Arequipa to Puno, 5 hours and 30 minutes more.
From Arequipa to Puno by bus
From Arequipa there are also different transportation companies that offer this service, the best known company is Cruz del Sur. The trip from Arequipa to Puno takes 5 hours and 30 minutes approximately.
From Colca Canyon to Puno by bus
In case you are going to visit the Colca Canyon, there is an option to take the bus in the town of Chivay. The company 4M offers buses that leave from the main square of Chivay and arrive in Puno in approximately 6 hours.
From Cusco to Puno by bus
In this case, there are two types of buses that you can use with commercial companies such as Cruz del Sur in tourist buses. In the case of commercial buses, the trip takes 6 hours and 30 minutes approximately. In the case of taking the tourist bus, the trip lasts approximately 10 hours and is called “La Ruta del Sol” (Route of the Sun), this tourist bus makes stops in places like Andahuaylillas, Raqchi, La Raya and Pucara.
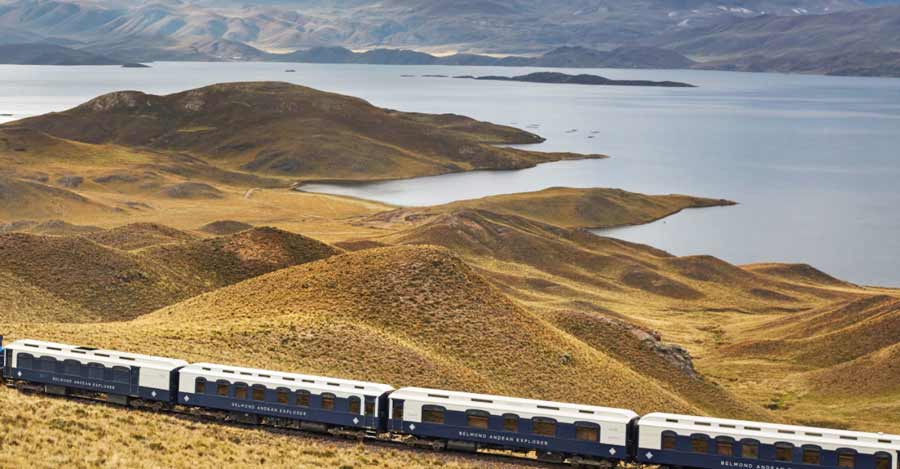
Traveling to Lake Titicaca in Puno by Train
In the case of this means of transportation, there is only one route to get from Cusco to Puno and visit the incredible Lake Titicaca. This is the most luxurious option to get to Puno.
Belmont Andean Explorer, the luxury train to Lake Titicaca
This train travels on one of the highest railway tracks in the world, with an altitude of over 4000 meters above sea level. It has wagons that come from the Australian Great South Pacific Express train conditioned to function as accommodations. The train has a maximum capacity of 48 passengers that can be distributed in 24 suites. Each suite has double or twin beds, private bathrooms, showers and other services. Within its facilities, there is a restaurant car, a bar car, an observatory car and a spa car.
Undoubtedly this is one of the best luxury trains in the world that already has international awards and takes us through beautiful landscapes to the lake Titicaca.
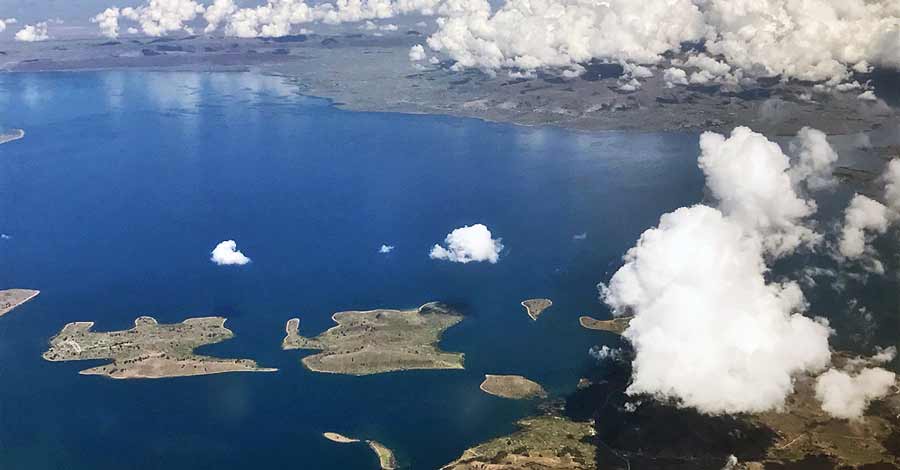
How many islands does lake Titicaca have?
Among the long list of islands that rest on the lake, we highlight some of them:
Sun Island: is the largest of the lake, its original name is Titikaka Island, along the island highlight archaeological sites of Inca manufacture, which highlights the “Sacred Rock” which is mentioned is the place of origin of the Inca civilization.
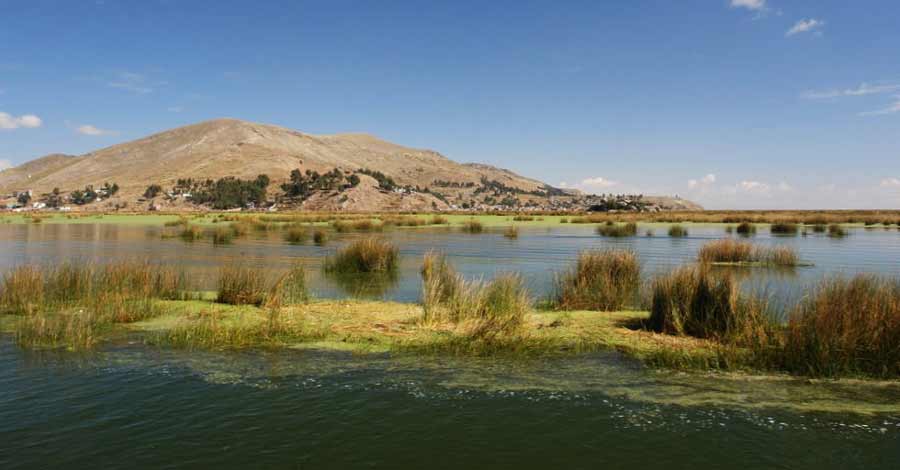
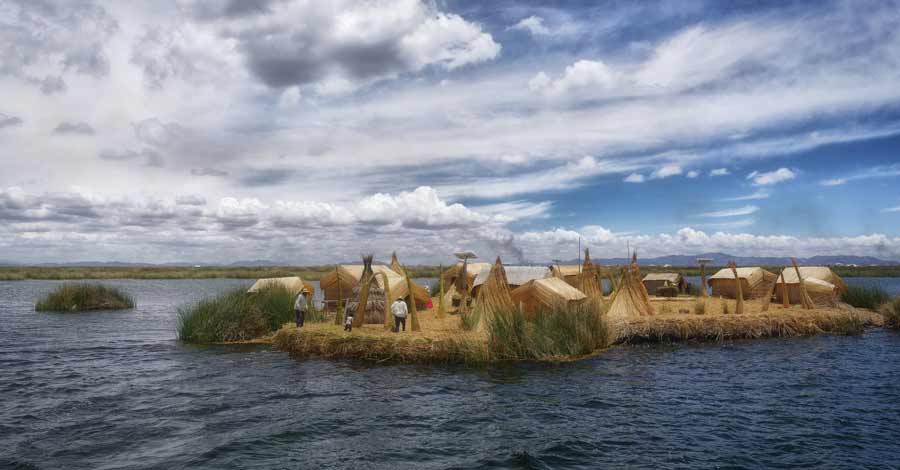
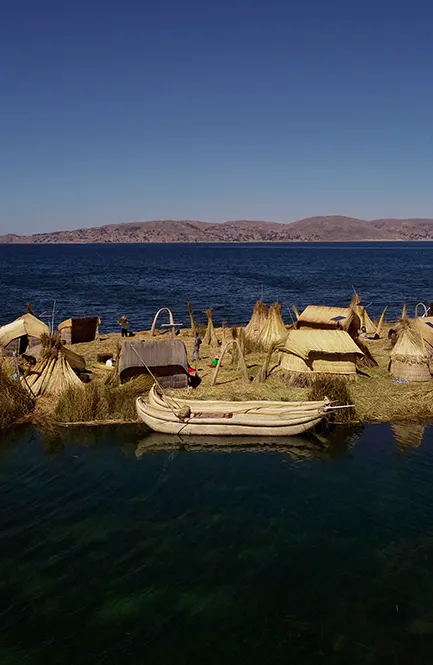
Uros Islands on Lake Titicaca
It is a long extension of artificial islands built based on Totora by the Uros ethnic group. It is an island where you can enjoy cultural, experiential and adventure tourism.
Taquile Island on lake Titicaca
The textile production of this island is considered a “Masterpiece of the oral and intangible heritage of humanity”, since its clothing preserves pre-Hispanic elements of the Andean Pukara, Colla and Inca societies. It is also the largest island of Lake Titicaca on the Peruvian side.
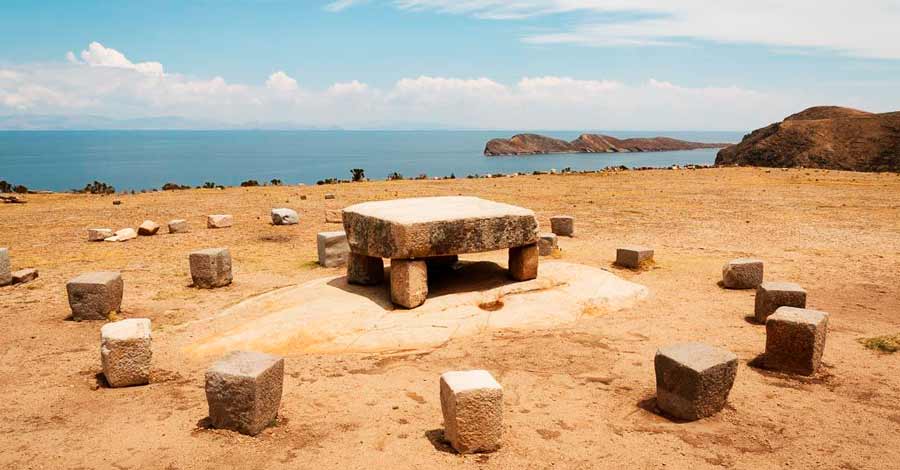
Isla del Sol (Sun island) on lake Titicaca
Sun Island is 9.6 km long by 4.6 km wide and has an area of 14.3 km², making it the largest island in Lake Titicaca. Its original name is Titicaca Island. This island is home to a number of myths and legends, including those of the origin of the Incas.
Among other islands, the island of Amantani on the Peruvian side or the island of the Moon on the Bolivian side also stand out, both with Inca archaeological vestiges.
Ruins in lake Titicaca
There are archaeological remains on the islands of Taquile and Amantani. But the one with more archaeological remains is undoubtedly the Isla del Sol on the Bolivian side of Lake Titicaca. On the Isla del Sol (Sun island) there are important archaeological sites such as Chinkana, Pilkokaina, the Sacred Rock, among others.
It is also known that there are 24 submerged archaeological sites on the Bolivian side, many of them predecessors of the Tiawanaco culture, one of the parent cultures of the Andean man. Some 10,000 archaeological pieces were also found underwater, including bone artifacts and kitchen utensils.
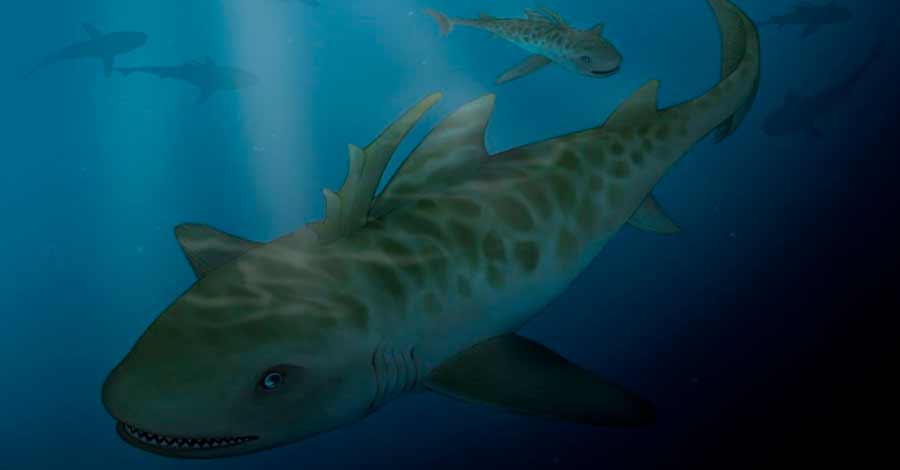
Are there sharks in lake Titicaca?
The question may seem very curious and even far-fetched, but the answer is partially affirmative. And is that in 2017 were found are the fossilized remains of a shark Pucapampella with an antiquity of 400 million years found on the shores of the lake, one of the oldest vertebrates in this part of the continent.
The finding was made by students from the University of Puno in the paleontological sites of Imarrucos, Taraco district, near the lake that delimits the border with Bolivia at 3,800 meters above sea level.
The remains found, which belong to the Devonian period, the Devonian period is known as “the age of fish” since in that period the first vertebrates (fish) appeared and from them evolved other groups such as amphibians and reptiles, which were in turn ancestors of mammals, said the Ministry of Culture. In other words, the existence of sharks in the Titicaca area is affirmative, but the Pucapampella shark corresponds to very ancient periods.
Is lake Titicaca the highest lake in the world?
If you surf the internet you will discover that many informative blogs and websites attribute to Lake Titicaca the title of the highest lake in the world. Even if people believe and claim that Lake Titicaca is the highest lake in the world, this statement is not correct, Lake Titicaca is the highest navigable lake in the world, different types of ships pass through it.
The highest lake in the world is in South America, but not between Peru and Bolivia but between Chile and Argentina. This lake is right in the area of the highest volcano in the world and receives the same name, “Ojos de Salado”.
The lake that has the same name as the volcano, Ojos de Salado, measures only 100 meters in diameter and has a depth of 5 to 10 meters. The lake is located at 6390 meters above sea level and in a crater.
What to do in lake Titicaca?
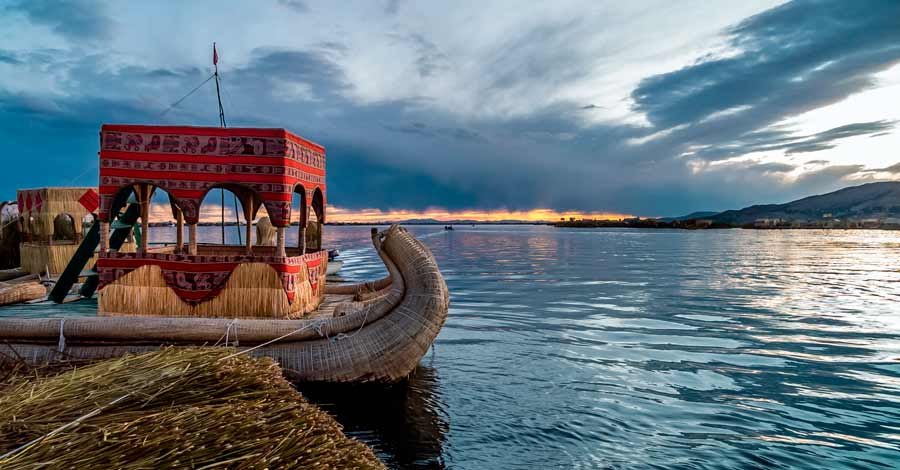
- Visit the curious floating islands of the Uros, whose inhabitants are dedicated to the millenary activity of weaving Totora fiber of Titicaca.
- Take a ride on the lake in the Caballitos de Totora, small traditional boats used by the natives for hundreds of years.
- Spend the night on the sacred island of Amantani.
- Visit Taquile, one of the most beautiful islands on a lake in the world.
- Explore the archaeological sites on the Isla del Sol (Sun Island).
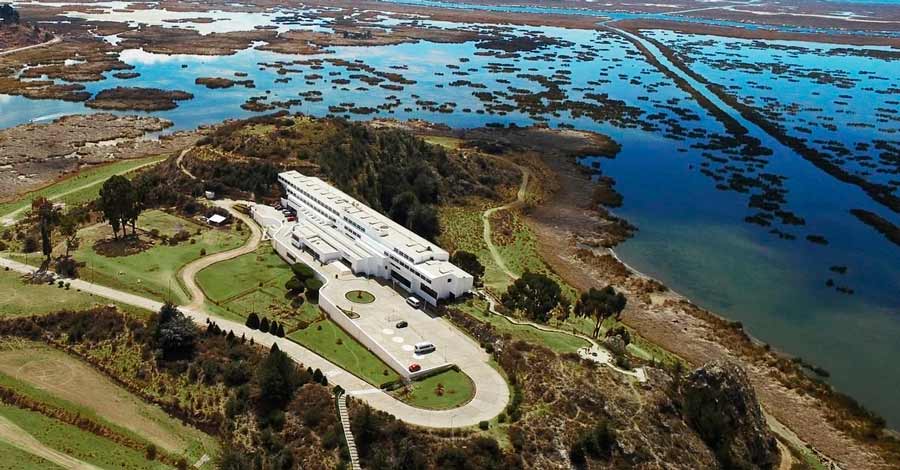
Lake Titicaca luxury hotels in Peru
GHL Hotel Lago Titicaca
GHL Hotel Lago Titicaca is located on the shores of the lake, on an island in lake Titicaca. GHL Hotel Lago Titicaca Puno offers a wellness center, a hot tub and a sauna. This hotel has views over Lake Titicaca and is located in the vicinity of Esteves Island.
Titilaka hotel
Within the unique landscape of Lake Titicaca, far from the beaten path, the Titilaka Lodge is a private retreat set on a private peninsula. It offers a splendid view of the lake from every room and the harmonious setting of contemporary decor that has managed to integrate the local heritage. Close to the village that gives it its name, it also allows you to discover the way of life and traditions of the lake’s inhabitants.
Casa Andina Premium Puno
It has 45 rooms a few steps from Lake Titicaca. You can enjoy exquisite gourmet breakfasts and a wide range of local dishes. It has different services such as bonfires in the evenings, perfect for travelers looking for a quiet place to rest.
Facts about lake Titicaca
- Titicaca is the second largest lake in South America after Lake Maracaibo in Venezuela.
- Lake Titicaca is the freshest lake in South America and is the 19th largest lake in the world.
- Lake Titicaca is the ancestral land of the Quechua, Aymara, Uros, Pacajes and Puquinas ethnic groups. The Uros still inhabit this island and its floating reed islands are a great tourist attraction of Lake Titicaca.
- Lake Titicaca is 56% Peruvian and 44% Bolivian, it is a binational lake whose traditions and myths are shared by both countries.
- The Titicaca we see today is the remnant of a gigantic lake or ancient sea. This internal sea receded to its present form. This process lasted thousands of years. The age of the current Lake Titicaca is estimated at 3 million years.
- In relation to the name of the lake, Titi, which means cat or puma, and kaka, stone. This would mean that Lake Titicaca means “the lake of the stone pumas” or “stone puma”.
- In 1973, the artificial satellite Gemini took the first photograph of Lake Titicaca from space, and it was discovered that the photograph of Lake Titicaca inverted has the shape of a puma or feline at the moment of catching its prey, a vizcacha.
- According to Andean tradition, Lake Titicaca was the place where the world was created, when the god Wiracocha, the supreme deity of the Andean culture, came out of the lake and created the sun, the stars and the first humans.
- The existence of sharks in the Titicaca area is affirmative, but these sharks, Pucapampella, inhabited the Titicaca area millions of years ago.
- There are 24 submerged archaeological sites on the Bolivian side of Lake Titicaca, many of them predecessors of the Tiawanaco culture.
Lake Titicaca is a very complete destination for all types of visitors, the lake is closely related to the history and tradition of all the ethnic groups that have inhabited this Andean area since ancient times. Apart from the great natural and cultural wealth that overflows in its waters, this area still preserves mysteries that still have no answer.
Therefore, to talk about Lake Titicaca is to enter a world full of mystery, myth, legends, history, nature and charm. Do not hesitate to plan your next trip to Lake Titicaca, the highest navigable lake in the world with Auri Peru, professionals who will customize your trip to the smallest detail and will make you live more than memorable experiences.